1. 자바 클래스를 작성하는 연습을 해보자. 다음 main() 메서드를 실행했을 때 예시와 같이 출력되도록 TV 클래스를 작성하라.
[결과]
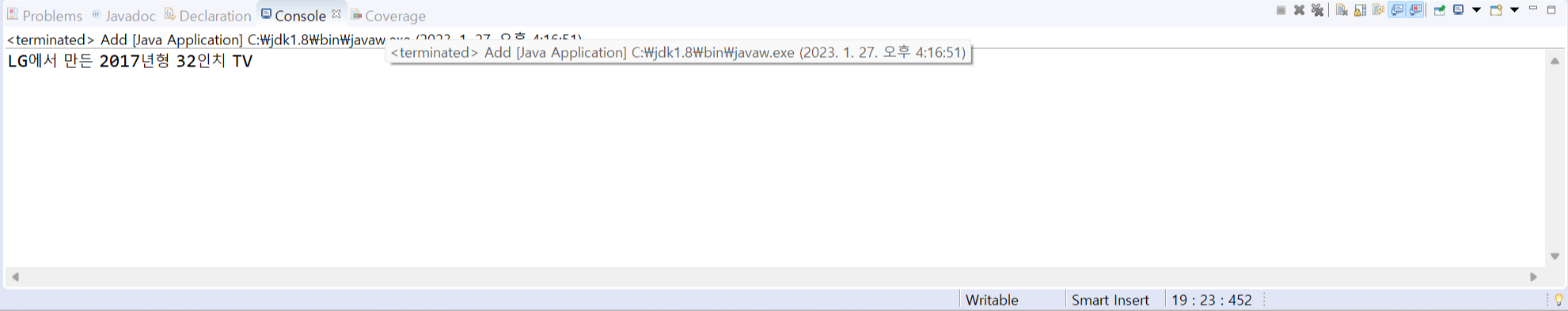
[소스 코드]
class TV{
private String manufacturer;
private int year;
private int inch;
public TV(String manufacturer, int year, int inch) {
this.manufacturer = manufacturer;
this.year = year;
this.inch = inch;
}
public void showTV() {
System.out.println(manufacturer + "에서 만든 " + year + "년형 " + inch + "인치 TV");
}
}
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV myTV = new TV("LG", 2017, 32);
myTV.showTV();
}
}
2. Grade 클래스를 작성해보자. 3 과목의 점수를 입력받아 Grade 객체를 생성하고 성적 평균을 출력하는 main()과 실행 예시는 다음과 같다.
[결과]

[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Grade{
int math, science, english;
public Grade(int math, int science, int english) {
this.math = math;
this.science = science;
this.english = english;
}
public int average() {
return (math + science + english) / 3;
}
}
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("수학, 과학, 영어 순으로 3개의 점수 입력 >> ");
int math = input.nextInt();
int science = input.nextInt();
int english = input.nextInt();
Grade me = new Grade(math, science, english);
System.out.println("평균은 " + me.average());
input.close();
}
}
3. 노래 한 곡을 나타내는 Song 클래스를 작성하라. Song은 다음 필드로 구성된다.
[결과]

[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Song{
private String title; //노래 제목을 나타내는 title
private String artist; //가수를 나타내는 artist
private int year; //노래가 발표된 연도를 나타내는 year
private String country; //국적을 나타내는 country
public Song() {} //기본 생성자와 매개변수를 가지는 생성자
public Song(String title, String artist, int year, String country) {
this.title = title;
this.artist = artist;
this.year = year;
this.country = country;
}
public void show() { //노래 정보를 출력하는 show() 메소드
System.out.println(year + "년 " + country + "국적의 " + artist + "가 부른 " + title);
}
}
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Song song = new Song("Dancing Queen", "ABBA", 1978, "스웨덴" );
song.show();
}
}
4. 다음 멤버를 가지고 직사각형을 표현하는 Rectangle 클래스를 작성하라
[결과]

[소스 코드]
class Rectangle{
private int x, y, width, height;
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public int square() {
return width * height;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("(" + x + ", " + y + ") 에서 크기가 " + width + " X " + height + "인 사각형 " );
}
boolean contains(Rectangle r) {
if(this.x <= r.x && this.y <= r.y && this.square() >= r.square()) {
return true;
}
else return false;
}
}
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(2, 2, 8, 7);
Rectangle s = new Rectangle(5, 5, 6, 6);
Rectangle t = new Rectangle(1, 1, 10, 10);
r.show();
System.out.println("s의 면적은 " + s.square());
if(t.contains(r)) System.out.println("t는 r을 포함합니다.");
if(t.contains(s)) System.out.println("t는 s을 포함합니다.");
}
}
5. 다음 설명대로 Circle 클래스와 CircleManager 클래스를 완성하라.
[결과]
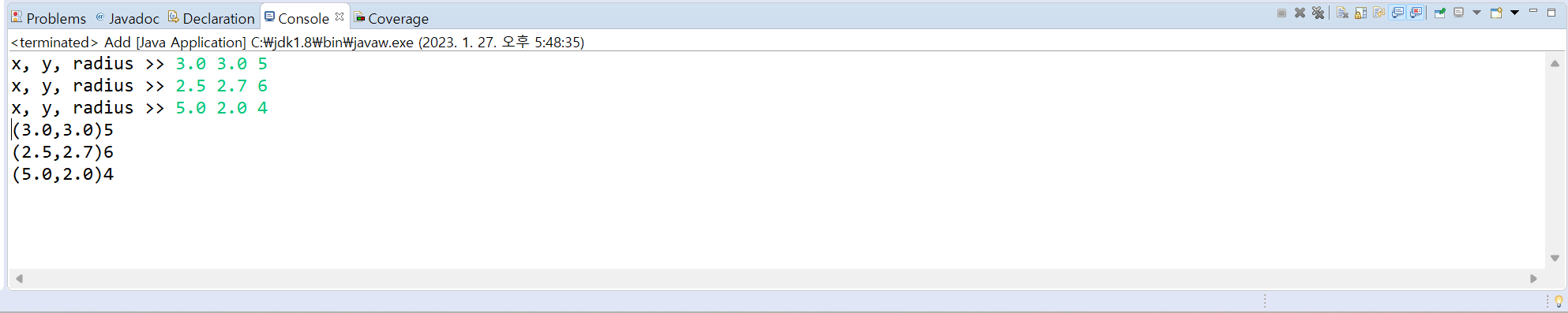
[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Circle{
private double x, y;
private int radius;
public Circle(double x, double y, int radius) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("(" + x + "," + y + ")" + radius);
}
}
public class CircleManager{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Circle c[] = new Circle[3];
for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
System.out.print("x, y, radius >> ");
double x = input.nextDouble();
double y = input.nextDouble();
int radius = input.nextInt();
c[i] = new Circle(x, y, radius);
}
for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
c[i].show();
}
input.close();
}
}
6. 앞의 5번 문제는 정답이 공개되어 있다. 이 정답을 참고하여 Circle 클래스와 CircleManager 클래스를 수정하여 다음 실행 결과처럼 되게 하라.
[결과]

[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Circle{
private double x, y;
private int radius;
public Circle(double x, double y, int radius) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.radius = radius;
}
public int getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("가장 면적이 큰 원은 (" + x + "," + y + ")" + radius);
}
}
public class App{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Circle c[] = new Circle[3];
for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
System.out.print("x, y, radius >> ");
double x = input.nextDouble();
double y = input.nextDouble();
int radius = input.nextInt();
c[i] = new Circle(x, y, radius);
}
int max = 0, maxRadius = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
if(maxRadius < c[i].getRadius()) {
maxRadius = c[i].getRadius();
max = i;
}
}
c[max].show();
input.close();
}
}
7. 하루의 할 일을 표현하는 클래스 Day는 다음과 같다. 한 달의 할 일을 표현하는 MouthSchedule 클래스를 작성하라.
class Day{
private String work;
public void set(String work) {this.work = work;}
public String get() {return work;}
public void show() {
if(work == null) System.out.println("없습니다.");
else System.out.println(work + "입니다.");
}
}MouthSchedule 클래스에는 Day 객체 배열과 적절한 필드, 메서드를 작성하고 실행 예시처럼 입력, 보기, 끝내기 등의 3개의 기능을 작성하라.
[결과]
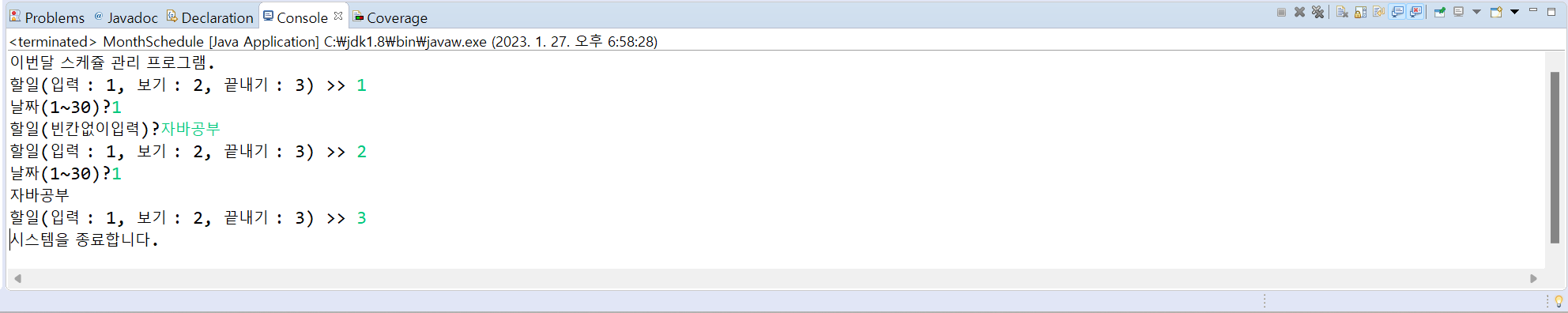
[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Day{
private String work;
public void set(String work) {this.work = work;}
public String get() {return work;}
public void show() {
if(work == null) System.out.println("없습니다.");
else System.out.println(work + "입니다.");
}
}
public class MonthSchedule{
Day day[] = new Day[30];
public MonthSchedule() {
System.out.println("이번달 스케쥴 관리 프로그램.");
for(int i = 0; i < day.length; i++) {
day[i] = new Day();
}
}
public void input(int date, String todo) {
day[date].set(todo);
}
public void view(int date) {
System.out.println(day[date].get());
}
public boolean finish() {
System.out.println("시스템을 종료합니다.");
return false;
}
public void run() {
System.out.print("할일(입력 : 1, 보기 : 2, 끝내기 : 3) >> ");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
MonthSchedule monthSchedule = new MonthSchedule();
boolean condition = true;
while(condition) {
monthSchedule.run();
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch(choice) {
case 1:
System.out.print("날짜(1~30)?");
int date = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("할일(빈칸없이입력)?");
String todo = scanner.nextLine();
monthSchedule.input(date, todo);
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("날짜(1~30)?");
date = scanner.nextInt();
monthSchedule.view(date);
break;
case 3:
condition = monthSchedule.finish();
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
8. 이름(name), 전화번호(tel) 필드와 생성자 등을 가진 Phone 클래스를 작성하고, 실행 예시와 같이 작동하는 PhoneBook클래스를 작성하라.
[결과]
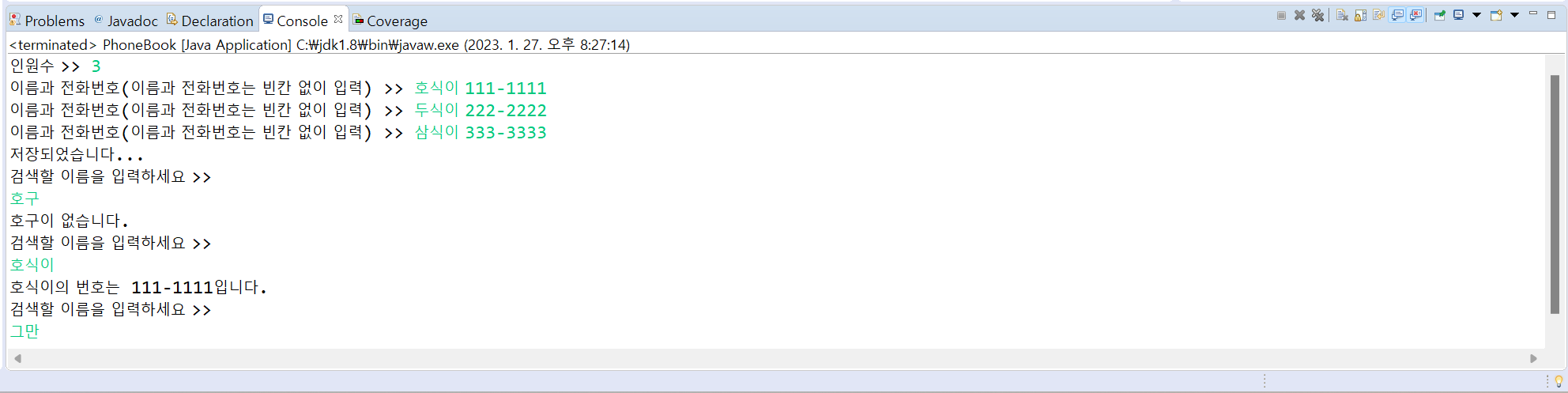
[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Phone{
private String name;
private String tel;
public Phone(String name, String tel) {
this.name = name;
this.tel = tel;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
}
public class PhoneBook{
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean condition = true;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("인원수 >> ");
int cnt = scanner.nextInt();
Phone phone[] = new Phone[cnt];
for(int i = 0; i < phone.length; i++) {
System.out.print("이름과 전화번호(이름과 전화번호는 빈칸 없이 입력) >> ");
String name = scanner.next();
String tel = scanner.nextLine();
phone[i] = new Phone(name, tel);
}
System.out.println("저장되었습니다...");
while(true) {
System.out.print("검색할 이름을 입력하세요 >> ");
String searchName = scanner.nextLine();
if(searchName.equals("그만")) break;
for(int i = 0; i < phone.length; i++) {
if(phone[i].getName().equals(searchName)) {
System.out.println(searchName + "의 번호는 " + phone[i].getTel() + "입니다.");
condition = false;
break;
}
else if(i == 2 && condition) System.out.println(searchName + "이 없습니다.");
}
}
}
}
9. 다음 2개의 static 가진 ArrayUtill 클래스를 만들어보자. 다음 코드의 실행 결과를 참고하여 concat()와 print()를 작성하여 ArrayUtill 클래스를 완성하라.
[결과]
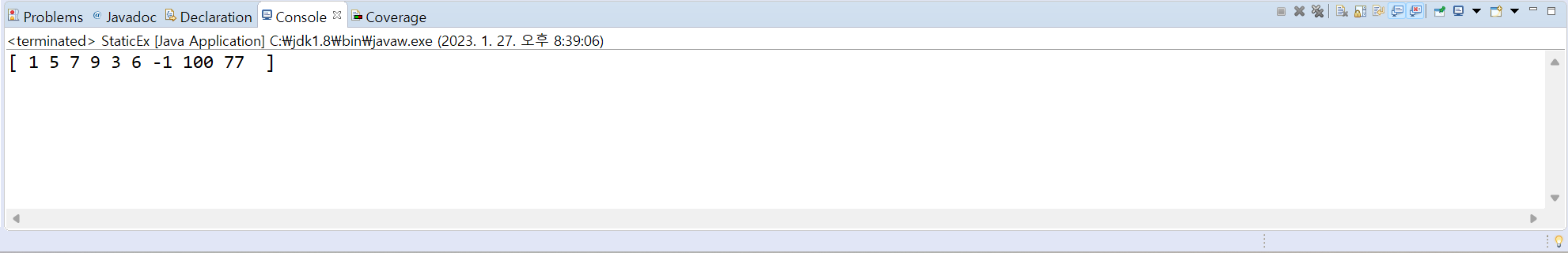
[소스 코드]
class ArrayUtill{
public static int[] concat(int[] a, int[] b) {
int size = a.length + b.length;
int concat[] = new int[size];
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
concat[i] = a[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
concat[i + a.length] = b[i];
}
return concat;
}
public static void print(int[] a) {
System.out.print("[ ");
for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i] + " ");
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
}
public class StaticEx{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array1 = {1, 5, 7, 9};
int[] array2 = {3, 6, -1, 100, 77};
int[] array3 = ArrayUtill.concat(array1, array2);
ArrayUtill.print(array3);
}
}
10. 다음은 같은 Dictionary 클래스가 있다. 실행 결과와 같이 작동하도록 Dictionary 클래스의 kor2Eng() 메서드와 DicApp 클래스를 작성하라.
[결과]
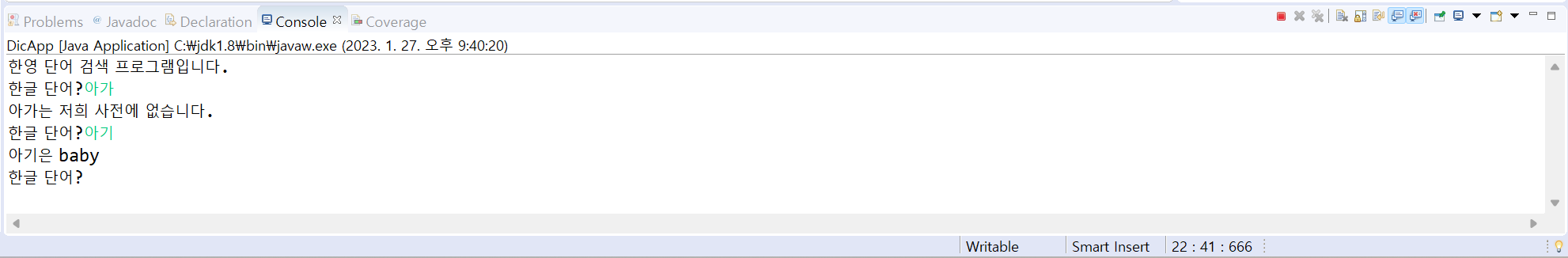
[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Dictionary{
private static String[] kor = {"사랑" , "아기", "돈", "미래", "희망"};
private static String[] eng = {"love" , "baby", "money", "future", "hope"};
public static String Kor2Eng(String word) {
for(int i = 0; i < kor.length; i++) {
if(kor[i].equals(word)) {
return word + "은 " + eng[i];
}
}
return word + "는 저희 사전에 없습니다.";
}
}
public class DicApp{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("한영 단어 검색 프로그램입니다.");
while(true) {
System.out.print("한글 단어?");
String word = scanner.nextLine();
if(word.equals("그만")) break;
System.out.println(Dictionary.Kor2Eng(word));
}
}
}
11. 다수의 클래스를 만들고 활용하는 연습을 해보자. 더하기( + ), 빼기( - ), 곱하기( * ), 나누기( / )를 수행하는 각 클래스 Add, Sub, Mul, Div를 만들어라. 이들은 모두 다음 필드와 메서드를 가진다.
- int 타입의 a, b 필드 : 2개의 피연산자
- void setValue(int a, int b) : 피연산자 값을 객체 내에 저장한다.
- int calculate() : 클래스의 목적에 맞는 연산을 실행하고 결과를 리턴한다.
main() 메소드에서는 다음 실행 사례와 같이 두 정수와 연산자를 입력받고 Add, Sub, Mul, Div 중에서 이 연산을 실행할 수 있는 객체를 생성하고, setValue()와 calculate()를 호출하여 결과를 출력하도록 작성하라.
[결과]
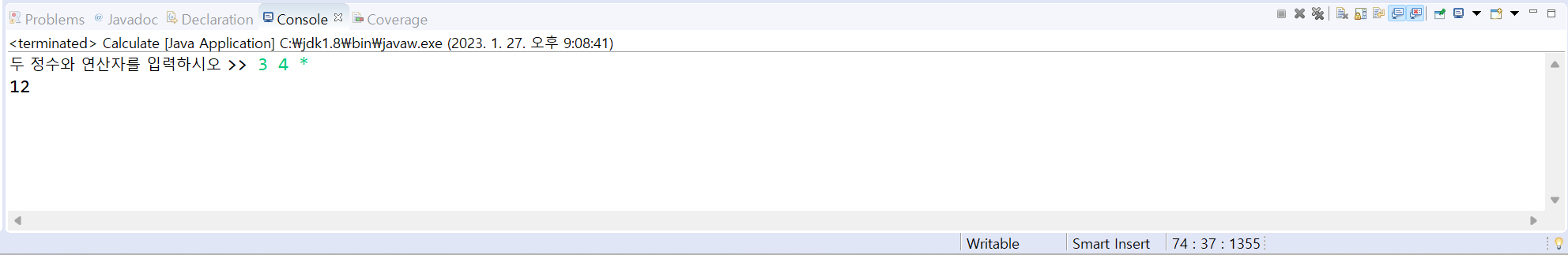
[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Add{
private int a;
private int b;
public void setValue(int x, int y) {
a = x;
b = y;
}
public int calculate() {
return a + b;
}
}
class Sub{
private int a;
private int b;
public void setValue(int x, int y) {
a = x;
b = y;
}
public int calculate() {
return a - b;
}
}
class Mul{
private int a;
private int b;
public void setValue(int x, int y) {
a = x;
b = y;
}
public int calculate() {
return a * b;
}
}
class Div{
private int a;
private int b;
public void setValue(int x, int y) {
a = x;
b = y;
}
public int calculate() {
return a / b;
}
}
public class Calculate{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("두 정수와 연산자를 입력하시오 >> ");
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int y = scanner.nextInt();
String operator = scanner.next();
if(operator.equals("+")) {
Add add = new Add();
add.setValue(x, y);
System.out.println(add.calculate());
}
else if(operator.equals("-")) {
Sub sub = new Sub();
sub.setValue(x, y);
System.out.println(sub.calculate());
}
else if(operator.equals("*")) {
Mul mul = new Mul();
mul.setValue(x, y);
System.out.println(mul.calculate());
}
else if(operator.equals("/")) {
Div div = new Div();
div.setValue(x, y);
System.out.println(div.calculate());
}
}
}
12. 간단한 콘서트 예약 시스템을 만들어보자. 다수의 클래스를 다루고 객체의 배열을 다루기에는 아직 자바 프로그램 개발이 익숙하지 않은 초보자들에게 다소 무리가 있을 것이다. 그러나 반드시 넘어야 할 산이다. 이 도전을 통해 산을 넘어갈 수 있는 체력을 키워보자. 예약 시스템의 기능은 다음과 같다.
- 공연은 하루에 한번 있다.
- 좌석은 S석, A석, B석으로 나뉘며, 각각 10개의 좌석이 있다.
- 예약 시스템의 메뉴는 "예약", "조회", "취소", "끝내기"가 있다.
- 예약은 한자리만 가능하고, 좌석 타입, 예약자 이름, 좌석 번호를 순서대로 입력받아 예약한다.
- 조회는 모든 좌석을 출력한다.
- 취소는 예약자의 이름을 받아 취소한다.
- 없는 이름, 없는 번호, 없는 메뉴, 잘못된 취소 등에 대해서 오류 메시지를 출력하고 사용자가 다시 시도하도록 한다.
[결과]

[소스 코드]
import java.util.Scanner;
class Sits{
private String sit;
public Sits() {
sit = "---";
}
public String getSit() {
return sit;
}
public void setSit(String name) {
sit = name;
}
}
class Line{
Sits sits[] = new Sits[10];
public Line() {
for(int i = 0; i < sits.length; i++) {
sits[i] = new Sits();
}
}
public void show() {
for(int i = 0; i < sits.length; i++) {
System.out.print(sits[i].getSit() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public void booking(String name, int num) {
sits[num - 1].setSit(name);
}
public void cancelBooking(String name) {
for(int i = 0; i < sits.length; i++) {
if(sits[i].getSit().equals(name))
sits[i].setSit("---");
}
}
}
public class BookSystem{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean condition = true;
System.out.println("명품콘서트홀 예약 시스템입니다.");
Line S = new Line();
Line A = new Line();
Line B = new Line();
while(condition) {
System.out.print("예약 : 1, 조회 : 2, 취소 : 3, 끝내기 : 4 >> ");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
switch(choice) {
case 1:
System.out.print("좌석구분 S(1), A(2), B(3) >> ");
int sit = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
switch(sit){
case 1:
System.out.print("S >> ");
S.show();
System.out.print("이름 >> ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("번호 >> ");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
S.booking(name, num);
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("A >> ");
A.show();
System.out.print("이름 >> ");
name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("번호 >> ");
num = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
A.booking(name, num);
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("B >> ");
B.show();
System.out.print("이름 >> ");
name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("번호 >> ");
num = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
B.booking(name, num);
break;
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("S >> ");
S.show();
System.out.print("A >> ");
A.show();
System.out.print("B >> ");
B.show();
System.out.println("<<조회를 완료하였습니다.>>");
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("좌석 S(1), A(2), B(3) >> ");
sit = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.nextLine();
switch(sit){
case 1:
System.out.print("S >> ");
S.show();
System.out.print("이름 >> ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
S.cancelBooking(name);
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("A >> ");
A.show();
System.out.print("이름 >> ");
name = scanner.nextLine();
A.cancelBooking(name);
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("B >> ");
B.show();
System.out.print("이름 >> ");
name = scanner.nextLine();
B.cancelBooking(name);
break;
}
break;
case 4:
condition = false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료합니다...");
scanner.close();
}
}'JAVA > 명품 JAVA Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [(개정판 4판) 명품 JAVA Programming] 5장 실습 문제 (0) | 2023.01.31 |
|---|---|
| [(개정판 4판) 명품 JAVA Programming] 5장 이론 문제 (0) | 2023.01.29 |
| [(개정판 4판) 명품 JAVA Programming] 4장 이론 문제 (0) | 2023.01.27 |
| [(개정판 4판) 명품 JAVA Programming] 3장 실습 문제 (0) | 2023.01.24 |
| [(개정판 4판) 명품 JAVA Programming] 3장 이론 문제 (0) | 2023.01.23 |